IDENTIFYING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Learning Outcomes
- Explain why competitive advantages are typically temporary.
- List and explain each of the five forces in Porter's Five Forces Model.
- Compare Porter's three generic strategies.
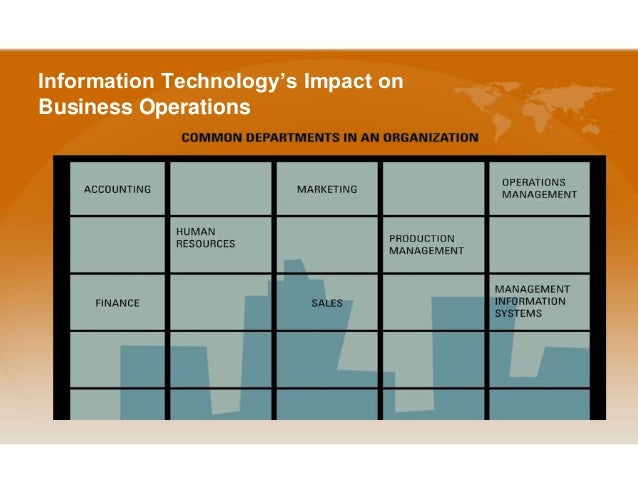
- Describe the relationship between business processes and value chain.
The Five Forces Model
1. Buyer power
Buyer power high when buyers have more choices to choose and low when their choices are few.
2. Supplier power
Supplier power is high when there are few choices to choose and low when there are many choice to choose
3. Threat of substitute products or services
Threat of substitute products or services high when there are many alternatives to a product and low when there are few alternatives from which to choose.
4. Threat of new entrants
High when it is easy for new competitors to enter a maket and low when there are significant entry barriers to entering a market.
5. Rivalry among existing competitors
High when competition is fierce in a market and low when competition is more complacent.
The Generics Strategies
1) Cost Leadership
- Becoming a low-cost producer in the industry allows the company to lower prices to customers.
- Competitors with higher costs cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price.
2) Differentiation
- Create competitive advantage by distinguishing their products on one or more features important to their customers.
- Unique features or benefits may justify price differences and stimulate demand.
3) Focus Strategy
- Target to a nice market.
- Concentrates on either cost leadership or differentiation.
The Value Chains-Targeting Business Processes.
- Supply Chain - a chain or series of processes that adds value to product & service for customer.
- Add Value - to its products and services that support a profit margin for the firm.